Introduction to Acetatas
Acetatas are intriguing compounds that fly under the radar in chemistry and materials science discussions. Yet, they play a vital role in various industries, from food preservation to pharmaceuticals.
If you’ve ever wondered how these versatile substances contribute to our daily lives or what makes them so unique, you’re in for a treat.
Dive into the world of acetatas as we explore their definition, chemical composition, and physical properties—shedding light on why they deserve more attention than usual!
Definition and background information
Acetatas, commonly known as acetates, are derived from acetic acid and are vital in various chemical processes and applications. They are formed when acetic acid reacts with alcohol.
The versatility of acetates is remarkable. They can be found in natural substances like cellulose acetate, often used in textiles and film production. Their synthetic counterparts are crucial in industries such as food preservation and cosmetics.
Acetatas have gained attention for their functional properties and eco-friendly alternatives to conventional materials. As sustainable practices become increasingly important, the demand for these compounds grows.
From industrial uses to everyday products, acetates offer unique benefits that make them indispensable across multiple sectors. Understanding their significance helps illuminate why they remain a topic of interest among chemists and manufacturers alike.
Chemical Composition:
Acetatas are fascinating compounds primarily known for their acetate anion (C2H3O2−). This simple yet versatile structure plays a crucial role in many chemical reactions.
The molecular formula of acetates is often represented as CnH2n+1COO−. Here, ‘n’ denotes the number of carbon atoms in the alkyl group. With this variability, acetates can form from various alcohols and acids.
Their unique arrangement allows them to participate in diverse applications across industries. The functional groups within these molecules contribute to both solubility and reactivity.
Understanding their composition opens doors to exploring their behavior under different conditions, further highlighting their importance in chemistry and beyond.
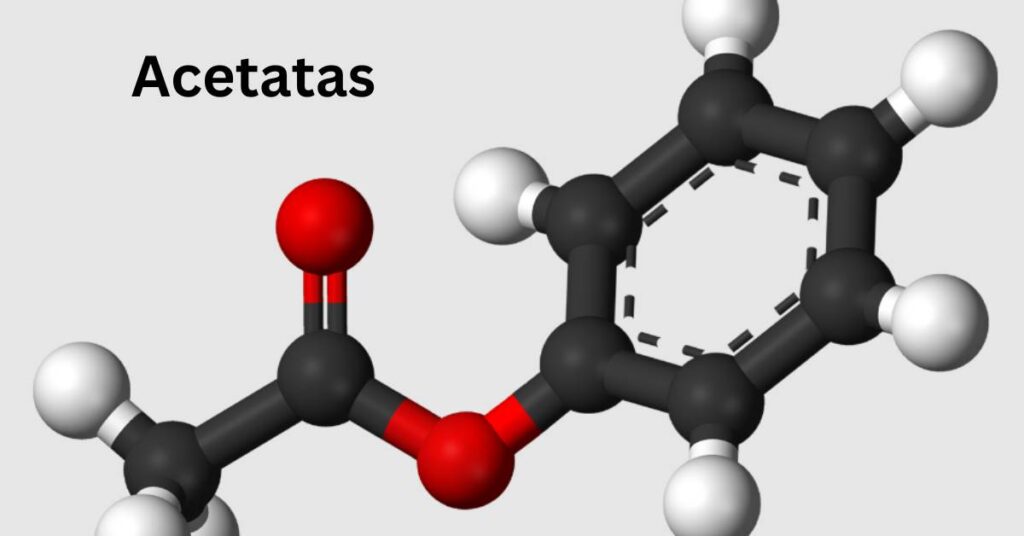
Explanation of its molecular structure
Acetatas, or acetate salts, have a fascinating molecular structure that plays a crucial role in their properties. They are derived from acetic acid and contain the acetate ion (C2H3O2-), formed when acetic acid donates a proton.
The acetate molecular formula can vary based on the metal cation it pairs with. For example, sodium acetate combines with sodium ions. The arrangement of atoms gives acetates unique characteristics that affect solubility and reactivity.
Regarding bonding, the carbon atoms in the acetate group are connected through single bonds to hydrogen and oxygen atoms. This configuration allows for flexibility in how these compounds interact with other substances.
Understanding this molecular framework opens doors to exploring their diverse applications across industries—from food preservation to pharmaceuticals. Each variation brings its own set of qualities influenced by its elemental makeup.
Physical Properties:
Acetatas, a versatile compound, exhibit fascinating physical properties. Depending on their specific form, they typically appear as colorless liquids or crystalline solids, making them easy to identify in various applications.
The texture of acetates can range from smooth and dense to granular, depending on the type. Their consistency often highlights their purity and quality.
When it comes to odor, many acetates possess a sweet or fruity scent that can be quite pleasant. This aromatic profile is particularly noticeable in acetate esters in food flavorings and fragrances.
These features make acetatas not just functional but also appealing for consumer products. Their unique combination of appearance and sensory properties contributes significantly to their widespread use across different industries.
Appearance, texture, and odor
Acetatas present a distinctive appearance that often varies depending on their specific form. When in solution, they are typically colorless or pale yellow liquids. In solid form, they may appear as white crystalline powders.
Acetates’ textures can range from smooth and dense to grainy, depending on the concentration and type of acetate being analyzed. This variance is significant in various applications, such as food preservation and industrial processes.
When it comes to odor, many acetates emit a pleasant fruity scent reminiscent of ripe fruits like apples or bananas. However, some might have less appealing odors due to impurities or specific chemical compositions.
This sensory profile makes them unique and valuable across different industries—from food product flavoring agents to laboratory solvents. Their versatility is evident not only in their uses but also in how they engage our senses.
Conclusion
Acetatas are fascinating compounds that play a vital role in various industries. Their unique properties make them versatile and highly useful in everyday applications.
Understanding their chemical composition gives insight into why they behave the way they do, while their physical characteristics highlight their practicality.
With diverse uses—from solvents to food additives—acetatas are essential in both industrial and commercial settings.
Exploring this compound enriches our knowledge of chemistry and its implications for modern life. Whether you’re a professional or simply curious, there’s always more to discover about acetatas and their impact on our world.
Latest post!
- Crossovericon.eu: Connecting Worlds Through Innovative Crossovers
- Why iFunTV is the Go-To Platform for Global TV and Movie Buffs
- M0therearf: A Deep Dive into Its Growing Popularity
- Dadiyanki: Exploring the History and Cultural Significance
- Tsumino: How This Platform Redefines Manga Browsing
- Sean Flaherty Obituary: Celebrating a Life Well Lived





